SESSION 4
PART 1
Electronic scales
Read the following text and answer the questions.
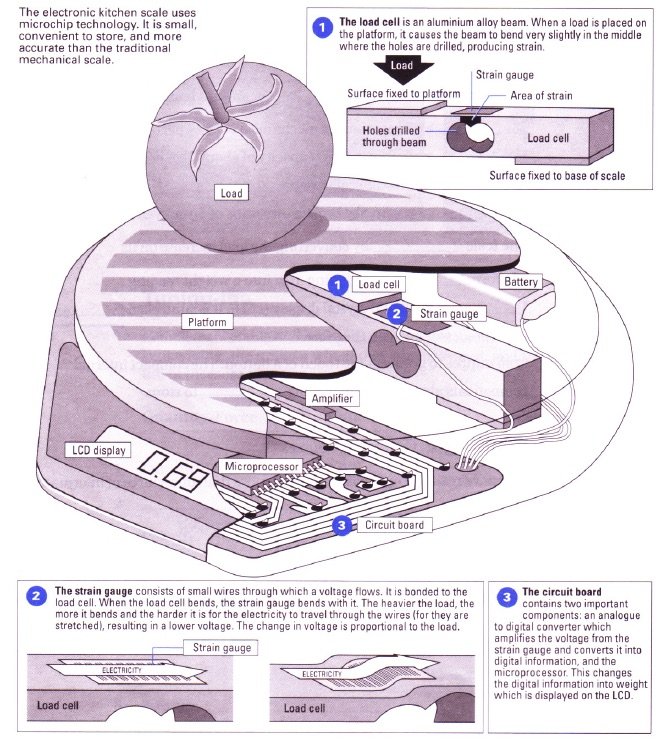
Electronic scales use a weighing device called a load cell underneath the platform. The load cell, an aluminium alloy beam, eliminates the need for springs, cogs, or other moving parts which can wear, break, or cause inaccuracy in mechanical scales.
A strain gauge is bonded on the load cell. The strain gauge consists of a small piece of metal foil which detects any bending of the beam. A controlled input voltage is supplied to the strain gauge from a battery powered circuit.
When a load is placed on the platform, it causes the load cell to bend very slightly. This in turn causes a change in strain, which triggers a change in the electrical resistance of the strain gauge.
As the resistance changes, so does the output voltage from the strain gauge. In short, the change in voltage across the strain gauge is proportional to the load on the platform.
The voltage from the gauge is small and has to be amplified and then converted into a digital signal. Under the platform, a circuit board holds the necessary components. First, an amplifier increases the amplitude of the signal. It is then fed to a specially programmed microprocessor, which converts it into a weight reading. This is displayed on the LCD. The display will automatically switch off a few minutes after weighing is finished, thereby saving battery power.
Adapted from “Inside Out: Electronic Scales”, Education Guardian,
in Oxford English for Electrical and Mechanical Engineering.
COMPREHENSION
1. Skim the text and focus on the verbs. Which tense is mostly used in process descriptions?
- at the frontier of Physics (2a) many (2b) .
- (3) students (4) in both the physics professions and in other fields...
2. Kristin Beck works...
- ...in (5)
- ...on a system aimed at studying how to make mediated (6) .
3. Laura Lopez
- She looks at (7) the went off in the last (8) , looking at (9) to better understand the physics of the explosion and how the explosion (10)
4. Wolfgang Ketterle at Center for Ultracold atoms:
- Collaboration between the (11) at MIT and Harvard.
- The (12) of his research group is (13) .
- Future: (14) .
5. Nergis Malvalvala, Laser and Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO):
- Main facilities (15) .
- Goal (16) .
- Future: regular detection of radiation from different sources in the sky to launch the era of gravitational wave astrophysics.
PART 2: Watch the video (02:28:00-end) and identify the main ideas/information mentioned by the following people.
INFORMATION
6. Sabrina Gonzalez Pasterski:
7. Prashanth Vendataram:
8. Christie Chiu:
9. Edward Mazenc: UROP
10. Katelin Schultz:
- Note:
- TLL = Teaching and Learning Laboratory
- TA = Teaching Assistant, graduate student who tutors undergraduates
- A lot of universities
- With TLL,
STRUCTURE
Reading comprehension
- Electronic scales
Comprehension
- Tenses
- Clear explanations
- Mood
- Why passive?
- Linkwords
Writing
- The refrigeration cycle
COURSEBOOK
If you wish to have a digital copy of your English handout you can download it from Madoc or here.
TESTS
LANGUAGE TEST (10%)
- Language tools (20 minutes)
WRITING TEST (40%)
- Reading comprehension
ORAL TEST #3 (50%)
- Presentation (15 minutes)
ONLINE ACTIVITIES
Online activities available on Madoc are compulsory and must be completed by session 6 at the latest.