The National Curriculum
Education in the UK follows the National Curriculum, which was introduced by the British government under the Education Reform Act (1988).
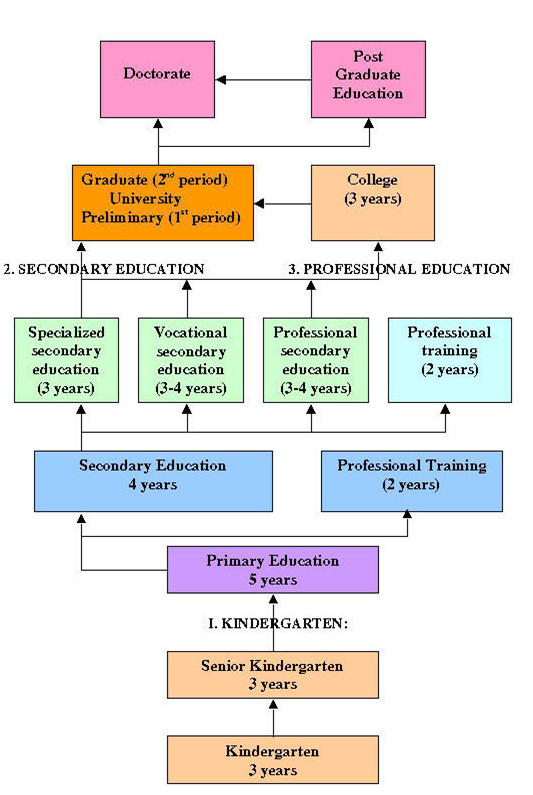
The education system in the United Kingdom varies in important respects between England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland. The Scottish Parliament and the assemblies in Wales and Northern Ireland have power over their own education system.
At the age of 16, students write an examination called the GCSE (General Certificate of Secondary Education, or O-level). All students are tested in mathematics, English, chemistry, biology, physics, history, one modern language, and one other subject, such as art or computer studies. A distinct but similar system exists in Scotland.
The A-level, short for Advanced Level, is a General Certificate of Education qualification in England, Northern Ireland and Wales, usually taken by students during the optional final two years of secondary school [Years 12 & 13 (usually ages 16-18)], commonly called the Sixth Form, after they have completed GCSE exams. The qualification is recognized around the world and is used as a sort of entrance exam for some universities.

Many companies sell programmes to prepare for the A-level test. Image from mathsmadeeasy.co.uk.
Undergraduate studies (before the Bachelor’s Degree)
- Bachelor’s degree
A bachelor's degree is an undergraduate academic degree awarded for a course or major that generally lasts for three years. The degrees awarded carry a designation related to the broad subject area such as BA (Bachelor of Arts), BSc (Bachelor of Science), BEng (Bachelor of Engineering), etc.
- Honours
A degree may be awarded with or without honours, with the class of an honours degree based on the average mark of the assessed work a candidate has completed. Below is a list of the possible classifications with common abbreviations.
- First-Class Honours (First or 1st)
- Upper Second-Class Honours (2:1)
- Lower Second-Class Honours (2:2)
- Third-Class Honours (Third or 3rd)
- Ordinary degree (Pass)
- Fail (no degree is awarded)

British undergraduate students. Image from studying-in-uk.org.
TEST YOURSELF
QUESTIONS
1. What type of school do British children go to when they are three years old?
2. How old do you have to be to leave school in England?
3. When was the current national curriculum approved?
4. What is the O-Level?
5. What is the A-Level?
6. Is there an official test to enter university in the UK?
7. What is a bachelor's degree?
8. What is a 2:1?
9. What is the difference between a BA and a BSc?
10. Why is an MRes longer than an MSc?
11. What is a PhD?
12. What may happen if doctorate students do not submit their theses in 4 years?

Secondary school students wearing uniform. Image from independent.co.uk

The famous Oxford vs Cambridge boat race. Image from theboatrace.org